A bone density test is a medical test that measures the strength and density of bones.
The test is used to diagnose osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle and are more likely to break.
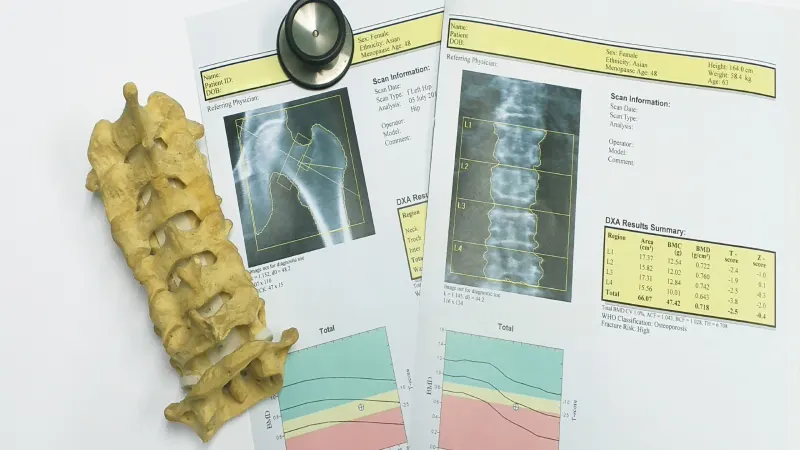
There are different types of bone density tests, but the most common is called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). During a DEXA scan, the patient lies on a table while a machine scans the hip, spine, or other bones. The test is quick and painless, with no preparation required.
The results of a bone density test are reported as a T-score, which compares the patient’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same gender.
A T-score of -1.0 or higher is considered normal, while a T-score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates low bone density (osteopenia), and a T-score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis.
Women over the age of 65 and men over the age of 70 are recommended to have it.
People with risk factors for osteoporosis, such as a family history of the disease, smoking, and long-term use of certain medications, may also be advised to have it at a younger age.The test is painless and non-invasive, but there are some things to keep in mind before and during the test.
Medications may also be prescribed to help slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
In conclusion, a bone density test is an important diagnostic tool for assessing bone health and diagnosing osteoporosis. By identifying individuals at risk for the disease, doctors can recommend interventions to help prevent fractures and improve bone health.
What is a bone density test?
It is a medical test that measures the strength and density of bones. It is used to diagnose osteoporosis and assess the risk of bone fractures.
How is a bone density test performed?
The most common type of it is called dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). During a DEXA scan, the patient lies on a table while a machine scans the hip, spine, or other bones.
Is a bone density test painful?
No, it is quick and painless, with no preparation required.